Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, unlike cervical and lumbar osteochondrosis, is very rare.
This is the structure of the thoracic region: it has more discs than the cervical and lumbar together, the discs are smaller and thinner. The mobility of this section is generally less, and the ribs and sternum take part of the load.
With osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, the symptoms can be mistaken, for example, for a heart attack. The reason for this is in the specific characteristics of the disease.
Painful pain during movement and exertion, as in cervical or lumbar osteochondrosis, is not present in this case, and complications associated with suspected angina pectoris or myocardial infarction or with impaired respiratory function come to the foreflat.
Reasons
To a greater extent, the development of osteochondrosis is favored by hypodynamics, a deficit of muscular loads, which forms the lack of training of the muscular corset, the weakening of its functions and an increase in the load on the ligaments and discsintervertebral.
The following conditions can also cause osteochondrosis:
- Incorrect posture and lateral curvature of the spine;
- Bad habits;
- Physical and nervous effort, stress;
- Back and spinal strain when wearing high heels, during pregnancy and flat feet;
- Back injuries;
- Hypodynamics;
- Inheritance;
- I work physically hard.
The intervertebral discs of the thoracic vertebrae are equally affected by a sedentary lifestyle and physical activity, increasing the likelihood of injury.
What is the specificity of the thoracic spine?
Everyone knows that the thoracic region is functionally inactive, particularly compared to the neck. And the load on him is not so great, in relation, for example, to the lumbar spine. For this reason, the appearance of a disease of the thoracic region rarely occurs with any symptoms at an early stage of development.
The low mobility of the thoracic spine is associated with its anatomical characteristics: the connection of the vertebrae with the ribs and the sternum makes it possible to create a sufficiently mobile and, at the same time, strong structure, which is less susceptible toinjuries and external influences.
The relatively small load in this department contributes to the fact that the appearance of any problems in it (for example, displacement of the vertebrae, intervertebral hernia, disc protrusion) is quite rare, this is confirmed by thestatistics. However, at the same time, their appearance cannot be called something extraordinary, for example, poor posture and scoliosis can be some kind of provoking factors that lead to the appearance of diseases of the spine.
At the same time, the symptoms of such diseases appear quite late and are quite typical of osteochondrosis; they usually represent compression of the nerve roots, in rare cases, compression of the spinal cord or its damage due to a violation of the blood supply, narrowing is also possible as a result of compression of the veins and arteries.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, the symptoms can be completely different, similar to the manifestations of other diseases of the internal organs. It is often thoracic osteochondrosis that is confused with coronary heart disease, cholecystitis, peptic ulcer, and even myocardial infarction and pneumonia. This is why this disease is called "chameleon".
Pain-related symptoms:
- The pain is localized below the shoulder blades, may radiate to the intercostal nerves. This leads to neuralgia. Pain increases when a person breathes, actively moves.
- Chest pain is most often on the left and may resemble ischemic heart disease. In this situation, it is important to find out in time the reason why the pain appeared. It is necessary to fully examine the cardiovascular system.
Neurological symptoms:
- Numbness or "goose bumps" in the legs, upper chest and abdomen (depending on the affected disc);
- Reflex tension in the chest or upper back muscles;
- In especially advanced cases, it is possible to disrupt the functioning of the pelvic organs, a decrease in potency in men.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, in addition to pain in the spine and back, near the site of location of osteochondrosis can also be pain in the upper abdomen, heart, liver, gallbladder.
With the appearance of such pain, sometimes it is possible that it is misdiagnosed. Pain on the right side of the chest below the ribs can be confused with inflammation of the gallbladder, on the left side of the chest; it can be confused with a heart attack. It is a mistake to confuse pain in the corresponding areas of the abdominal cavity with the manifestation of a stomach ulcer or gastritis.
Dorsago
Dorsago is one of the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, manifested by acute pain. Usually this symptom occurs in people who sit for a long time in one position or in an awkward position, with monotonous performance of monotonous work.
You may feel pain in your spine in your thoracic region, your muscles tense, and you often have trouble breathing. Intercostal neuralgia can occur.
Back pain
The exacerbation period will last between 2 and 3 weeks. In this case, the painful sensations gradually increase. Mild pain appears in the affected spine. As a rule, pain is especially actively manifested with deep breathing and bending forward, back, sideways.
The nature of back pain can be very different. Pain can be drawing, burning, aching, cutting, can be administered under the leg, arm, buttock, or shoulder blade. In terms of location, the pains are no less varied. They can appear below, above, in the middle, on the right, on the left, between the shoulder blades.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
When designing a treatment plan that determines how to treat osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, diagnostic data based on an X-ray examination helps. Such an examination gives a clear idea of how to treat thoracic osteochondrosis, because X-ray readings that indicate the growth of vertebral bodies and the presence of changes in intervertebral distance (decrease in height) are a characteristic symptom of this disease.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine depends on the stage of the disease and is mainly reduced to conservative therapy. Surgery is extremely rare in the case of a spinal hernia.
Medications
Drug therapy is based on the following principles:
- Use of a special medicine that allows fluid to retain within the intervertebral disc.
- Vitamins. Most often, complete vitamin complexes or preparations with the group of elements B are prescribed
- Antispasmodics and muscle relaxants that reduce spasms of the muscles around the spine.
- Painkillers. NSAIDs and analgesics based on drug combinations.
- Chondroprotectors. Essential to catalyze the repair process of damaged cartilage.
After elimination of acute events, massage of the muscles of the back and lower extremities is applied. Manual therapy is indicated at 1-3 degrees of osteochondrosis in the case of the development of functional blocks. Includes several options for soft and harsh effects on the back muscles.
The duration of treatment for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine depends on the severity of the disease and the degree of age-related changes, as well as the diligence of the patient to comply with the doctor's prescriptions.
Gymnastics for thoracic osteochondrosis
In case of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, patients are prescribed recovery gymnastics, the main purpose of which is to increase the mobility of the costal-vertebral and intervertebral joints. Exercise therapy (subject to regular and correct exercise) allows you to eliminate even very strong muscle spasms. Moderate physical activity will help relieve the stiffness in the spine, which occurs with a weak muscle brace.
Daily sessions, supervised by an experienced instructor, will have a beneficial effect on the whole body in general, and the bronchopulmonary system in particular. Patients have improved ventilation of the lungs and can breathe deeply and exhale without pain.
Massage

Massage not only weakens the severity of the symptoms of the disease, but also helps the person to recover, efforts are a positive effect of other elements of complex therapy.
It is prescribed individually depending on the clinical picture of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, the presence of chronic diseases and contraindications.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy is used to eliminate muscle hypertonicity and spasms, as well as to restore back mobility. Manual therapy helps to free blood vessels, improve nutrition and oxygen supply to the intervertebral disc tissues.
Correct position at rest and during sleep
For the prevention of osteochondrosis and during the treatment period, it is necessary to organize the correct position at rest and sleep. It is best if you sleep on a hard flat bed, but lest this be fanatic, if the bed does not meet the requirements, sleeping on the floor is not recommended, as you can catch a cold. This measure is very necessary so that the spine can quickly regain its normal shape.
However, a rather intense painful sensation may appear initially, which persists until the vertebrae assume a physiological position. To relieve pain and discomfort, you can place a roller under the affected area.
Exercises
The most effective treatment for muscle spasms is physical therapy. Well-chosen exercises relax and, at the same time, strengthen and train the back muscles. As a result, the thoracic spine is stabilized, the strangulated spinal nerves are released.
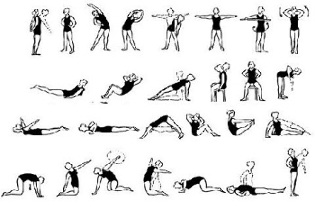
The set of exercises for thoracic osteochondrosis is performed as follows:
- Starting position - while inhaling, stand up straight, legs together, arms down. Stretch your arms up, exhale, then lean back and breathe deeply. Lower your arms, lean forward, circle your back, and lower your shoulders and head; exhale. Do 8 to 10 repetitions.
- Starting position: sitting in a chair. Slowly bring your hands behind your head: inhale, lean back 5 times, leaning against the back of a chair with your shoulder blades, exhale.
- Starting position: get on all fours and bend your back as much as possible, hold for 3 seconds, keep your head straight for three. Do 5 to 7 repetitions.
- Starting position: it is comfortable to lie on your stomach and place your hands on the floor. At the same time, lean back strongly and try to yank your body off the ground. Do 5 to 8 repetitions.
- Initial position: lying face down with arms extended along the body. Bend your chest, trying to lift your head and legs as high as possible. Do 5 to 8 repetitions.
By following all of your doctor's prescriptions, you can slowly but surely achieve significant improvement.
Prevention
The health of the chest and other parts of the spine can be impaired by:
- long static charges (sitting in front of the TV, computer);
- weight lifting;
- habit of stooping;
- hypothermia and frequent colds.
Office workers who sit in the workplace due to their duty of service need to change their body position more frequently, get up and do physical exercises. Even simple stretching is beneficial.



































